Thousands of startups close down every single year, but what percentage of them fail?
Over 305 million startups are created every year around the globe, and the majority of them don’t last long. There are many reasons why startups fail as it’s difficult for emerging companies to find a place in the market, compete with established competitors, and make a profit—let alone just break even.
If you’re curious about what percentage of startups fail, you’ve come to the right place. Read on for 45 startup failure statistics that dive into the top. This article will share top statistics, outline the industry, break down common failure reasons, and so much more.
Ready? Let’s go!
The top 10 startup failure statistics
- 9 out of 10 startups fail
- 38% of startups fail because they run out of cash
- 35% of startups fail because there is no market need for them
- By year 5, 50% of all startups will have failed
- 81% of startup owners are okay going into debt for their business
- 60% of startups fail between the pre-seed and Series A funding stages
- Approximately 35% of Series A startups fail before they reach Series B
- Roughly 80% of tech and eCommerce startups will fail
- 25-30% of VC-backed startups still fail despite extra funding
- Almost all startup “unicorns,” 99.9%, will fail
Why do 90% of startups fail?
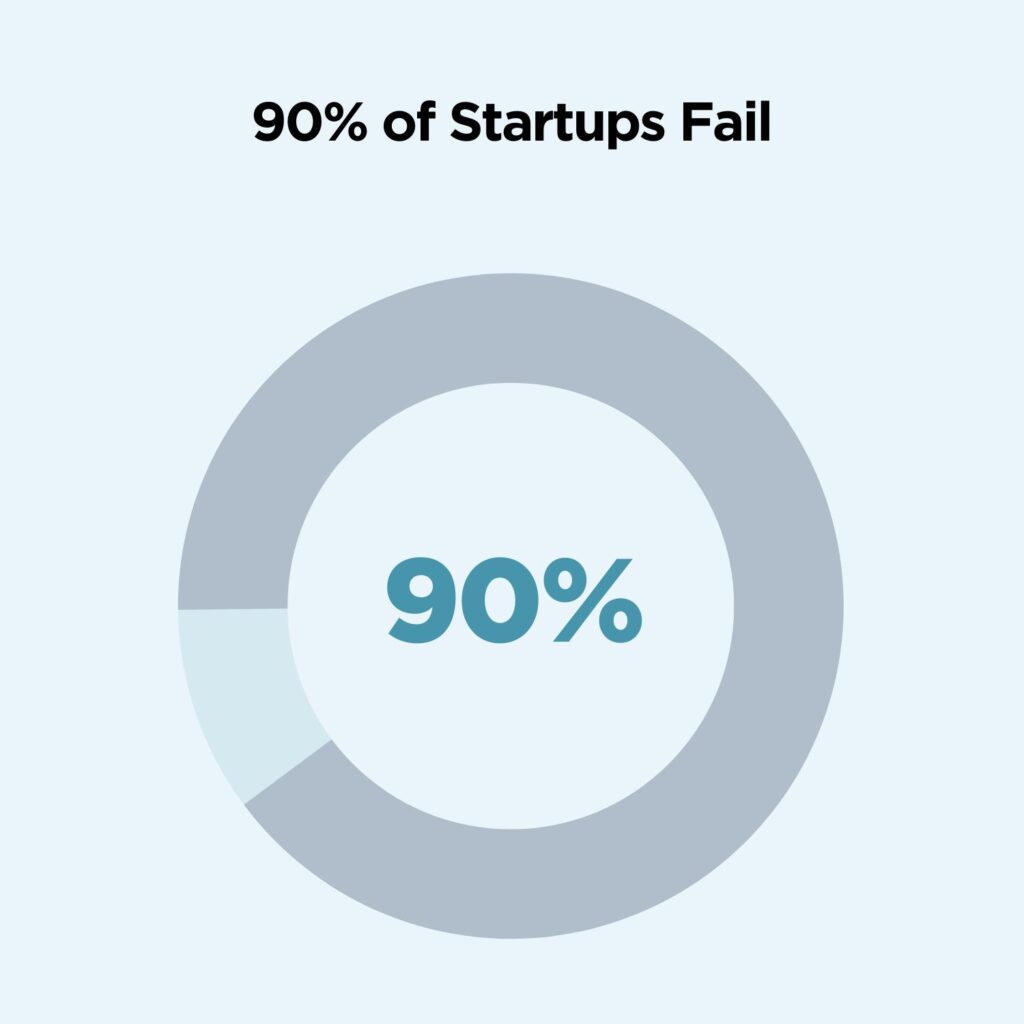
1. 9 out of 10 startups fail
(Failory)
The failure rate of startups is high at more than 90%. Over nine in 10 startups fail overall, and about 20% of those fail in the first year of operations.
2. All businesses have a 70% failure rate
(Nanoglobals)
Startups are especially likely to fail due to their innovative nature, but so are all business types. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labour, all businesses have a 70% failure rate in the long term. This failure rate escalates to 50% by the end of year five and jumps to 70% by year ten.
3. Startups take 2-3 times longer to validate their place in the market than founders expect
(Failory)
One of the biggest reasons why startups fail is that founders overestimate their products. Finding the market fit of a new startup takes 2 to 3 times longer than many founders anticipate. Meanwhile, founders often overestimate the value of their intellectual property before product-market fit—by as much as 255%.
4. Only 1 in 12 entrepreneurs succeeds in building a successful business
(Nanoglobals)
A published research study from 2019 revealed only 8.3% of entrepreneurs actually build a successful business. This translates to just 1 in every 12 entrepreneurs.
How many startups fail in the first 5 years?
5. More than 50% of startups fail in their first 5 years
(Failory)
When do startups most commonly fail? In their first five years. By the end of year five, a reported 50% of startups have failed.
What are the most common reasons why startups fail?
6. 38% of startups fail because they run out of cash
(CB Insights)
What is the #1 reason that startups fail? One simple word: money. An estimated 38% of startups fail because they run out of cash and fail to raise new, necessary capital.
7. 35% of businesses fail because there is no market need
(CB Insights)
Research shows that over one-third, 35%, of startups fail because there is no market need for their product. Sadly, this is something that could be avoided with proper market research and establishing an MVP (minimum viable product) to test their product fit before launching.
8. 20% of startups fail because they get outcompeted
(CB Insights)
Aside from misconstrued founders and poor market fit, one in five startups fail because they can’t beat out their competition. Other top reasons for startup failures include flawed business models (19%), regulatory/legal challenges (18%), pricing issues (15%), and poor teams (14%). Another 10% of startups fail because their product or service was mistimed.
| Failure reason | Percentage |
| Cash flow | 38% |
| No market fit | 35% |
| Competition | 20% |
| Business model | 19% |
| Regulatory challenges | 18% |
| Pricing issues | 15% |
| Team | 14% |
| Timing | 10% |
9. Entrepreneurs spend around 40% of their time on tasks that don’t generate income
(Entrepreneur)
Those working for a startup wear many hats, especially their founder(s). Most small businesses are fewer than 25 employees, leading many entrepreneurs to spend time on tasks that aren’t directly generating revenue for the startup. A recorded 40% of an entrepreneur’s day is spent on time-sucking duties like HR and payroll.
10. 81% of startup owners are comfortable going into debt for a business
(Lending Tree)
Running out of money is the top reason why startups fail and that’s largely due to the fact that many startups are funded by their owner’s personal finances. It turns out most prospective business owners, 81%, are willing to take on a debt too. In addition, 82% of owners said they’d take a pay cut for one year to work on their startup.
11. 1 in 3 would-be business owners say “general anxiety and fear of failure” discourage them from starting a business
(Lending Tree)
According to a survey, the biggest barrier for launching a startup is lack of money. While 40% said that cash was a problem, another 33% of adults said the top reason they hesitated was general anxiety. So, the “fear of failure” stops 1 in 3 adults from starting a business.
12. 93% of small business owners calculate a potential run-rate of less than 18 months upon launch
(Small Biz Trends)
More than nine in 10 business owners start a business with such little cash or funding, the estimated run-time is under 18 months. That means failure is imminent if the business doesn’t produce results immediately, further proving the riskiness of startup failure.
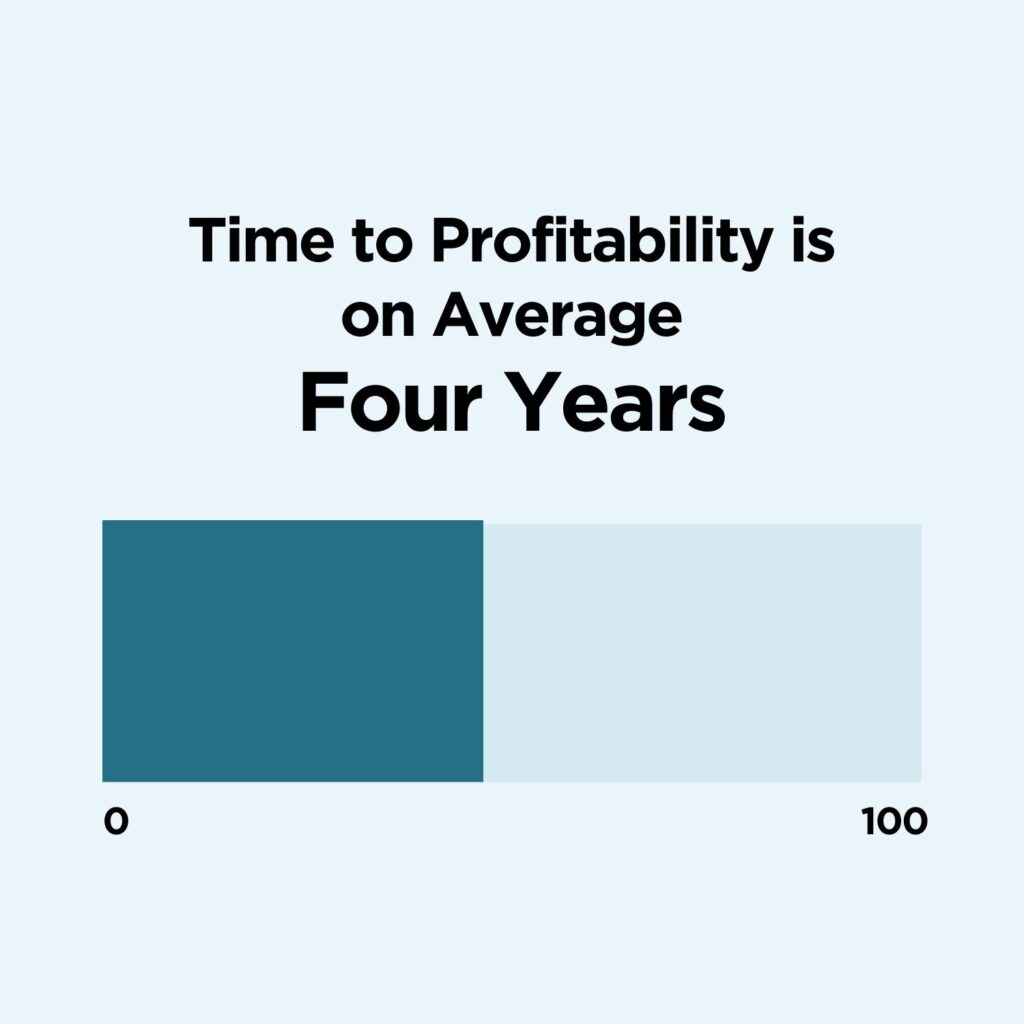
13. The average startup business takes about 4 years to make money
(Earthweb)
The average startup takes an average of 4 years to be profitable. Statistics show it usually takes seven to 10 years to create a “steady money-making business.” However, there are notable exceptions like Ford automobiles that took just 5 months to make a profit or Apple that took two years.
Startup failure rate by stage
14. One in five startups, 20%, fail by the end of their first year
(Failory)
Approximately 20% of startups fail by the end of their first year. Why do so many startups fail so quickly? Startups are often testing new products or services that haven’t been proven before. These new companies are serving undefined markets, feeding the statistic that 90% of all startups will inevitably fail.
15. 30% of startups will fail by the end of year 2
(SBA)
Approximately 30% of new small businesses fail by the end of year two, while half will fail before year five. That means roughly 70% of startups fail within their first five years of operations.
16. Only 30% of startups will survive more than ten years
(SBA)
The SBA reports that 70% of small businesses fail before their 10th birthday. However, it’s worth noting that many registered small businesses are not true startups, especially a decade into operation.
| Years in business | Percentage (failed startups) |
| Year 1 | 20% |
| Year 2 | 30% |
| Year 5 | 50% |
| Year 10 | 70% |
17. 60% of startups fail between pre-seed and Series A funding stages
(SPD Load)
There are three note-worthy stages for startups: pre-seed, Series A, and maturity. The average pre-seed stage startup usually gets between $50,000 and $200,000 within a fundraise of 3 to 9 months. About 60% of companies that raise pre-seed funding fail to make it to the next startup stage, Series A.
18. Approximately 35% of Series A startups fail before Series B
(SPD Load)
What percentage of startups fail after Series A? If a startup makes it to Series A, about 35% will fail before raising a Series B round. For the 65% of Series A startups that are able to raise capital, this stage typically brings in between $500,000 and $3 million within a period of 12 to 18 months.
19. After Series C, a startup’s chance of failing is low, about 1 in 100
(SPD Load)
As startups progress through funding stages into maturity, they are less and less likely to fail. According to research, the chance of failing for a startup past Series B is about 1%. Most Series B startups are valued between $30 million and $60 million. For context, the average Series F startup is valued around $400 million.
| Series | Failure rate |
| Pre-Seed/Series A | 60% |
| Series B | 35% |
| Series C | 1% |
Startup failure rate by industry
20. Roughly 80% of eCommerce startups fail
(SPD Load)
In 2021, global eCommerce sales reached $3.1 trillion and are growing year over year. Although this high number of sales doesn’t equate to success for eCommerce startups, considering this industry has a failure rate of about 80%.
21. More than 75% of Financial Technology (Fintech) startups fail
(SPD Load)
Statistics suggest that about three-quarters of startups in the financial technology space fail. This includes popular industries like mobile banking, cryptocurrency, and investment apps. Surprisingly, the majority of these Fintech startups fail, even after they secure VC funding.
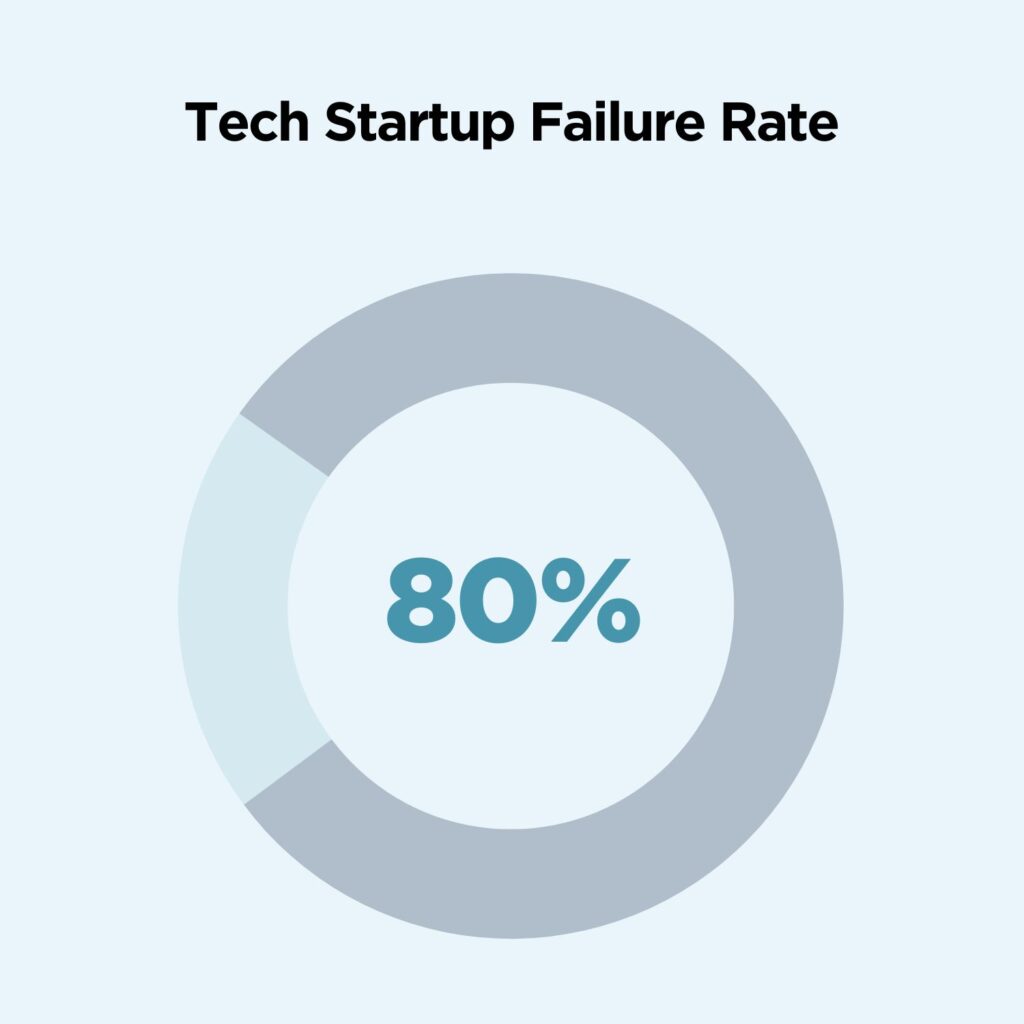
22. The tech startup failure rate is as high as 80%
(SPD Load)
How many tech startups fail? The vast majority of them. The “tech” industry covers a wide range of startups, but let’s break that down. Statistics reveal that up to 80% of HealthTech startups fail while 60% of EduTech startups close. Within the Gaming industry, startups have a higher chance of survival with around a 50% failure rate.
23. 90% of disruptive startups fail
(Nanoglobal)
Startups classified as “disruptive” have a higher failure rate because of their forward-thinking and potentially disruptive nature. Experts believe it’s these risky business ideas that fuel the 90% failure rate of startups.
Venture capital startup failure statistics
24. Only 0.05% of startups get VC funding
(CB Insights)
Venture capital is defined as a temporary equity investment in young, innovative, non-listed companies, aka startups. Many promising startups seek venture capital as a way to secure investment, but it’s extremely competitive and rare. A mere 0.05% of startups get VC funding.
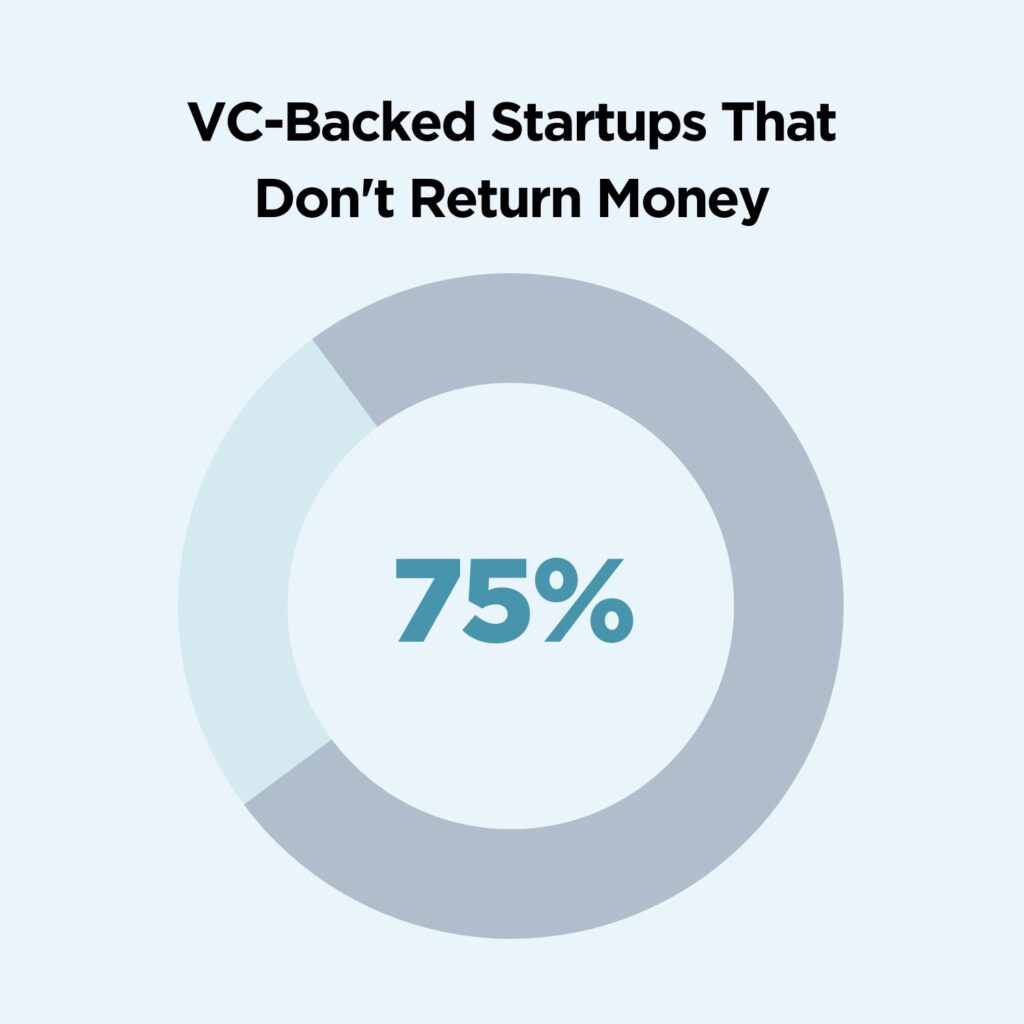
25. 75% of venture-backed companies never return cash to investors
(Failory)
Startups certainly use the capital they raise, but often don’t return it. Research shows that three in four startups backed by VC never end up returning their cash to investors. Meanwhile, as many as 30-40% of investors never get back their entire initial investment from a startup.
26. Less than 5% of startups break even on cash flow
(The Wall Street Journal)
Less than 5% of startups succeed enough to meet a specific revenue growth rate—or even break even on cash flow. An estimated 30-40% of high-potential startups fail as far as needing to liquidate all assets, as well as investors losing all of their original invested money.
27. 25-30% of VC-backed startups still fail
(The Wall Street Journal)
Experts from The National Venture Capital Association estimate that 25% to 30% of startups backed by VC funding go on to fail. As a general rule of thumb for startups, out of every 10, about three or four fail completely. The other three or four return their original VC investments, and only one or two will produce substantial returns.
28. The average investment check from a VC firm is $2.6 million for seed stage companies
(Fundable)
Statistics show there are around 462 active venture capital firms that invest in around 3,700 deals per year. Although a tiny percentage of companies are ever funded by a VC, the average investment size is noteabout at around $2.6 million to seed stage startups.
29. Only 6% of startups featured on the tv show, Shark Tank, fail
(Failory)
Companies that go on the popular reality TV show, Shark Tank, live to see very different futures. An estimated 94% of Shark Tank companies succeed and only 6% of these startups fail.
30. Venture capitalists are investing more than $333 billion in startups
(Statista)
Last year set a new record for venture capital investments within the U.S. Approximately $333 billion was invested, nearly twice as much as in 2020. This valuation is a cumulation of over 15,500 VC deals, another high point in venture capital U.S. history.
31. In Q1 of 2021, VC investments in the internet industry amounted to $25.9 billion
(Statista)
The internet industry is the leading segment of startups raising VC funding. The second leading venture capital sector in terms of investment was healthcare raising approximately $12 billion. Other notable industries for startups and VC funding include computer hardware and services, and mobile and telecommunications.
32. In the past decade, the global average of Series A rounds has tripled to more than $18 trillion
(Startup Genome)
Since 2012, startups are raising an average of about 3 times as much during Series A rounds. North America accounted for less than half of the early-stage funding raised in 2021, letting Europe and Asia make up the majority. Meanwhile in the past year, the VC activity in Latin America reportedly doubled.
Unicorn startup failure rates and statistics
33. 99.9% of unicorn startups fail
(Nanoglobal)
Companies become a “unicorn” once they reach a valuation of over $1 billion, without going public on the stock market. Only 0.00006 of startups reach unicorn status. As rare as they are, there are plenty of unicorn startups that have become household names, like Google, Canva, Space X, Instacart, Grammarly, and Airtable.

34. As of October, 2022, there were over 1,200 unicorns worldwide
(Startup Genome & CB Insights)
Last year in 2021, an unprecedented record of 540 companies achieved their “unicorn” status globally. These billion-dollar brands are located across 113 ecosystems worldwide, but most are in North America largely due to the location and attraction of Silicon Valley. As of now, there are approximately 1,200 unicorns globally.
35. North America is home to the most “unicorn” startups, with about 312
(Startup Genome)
North America is now home to 312 startup unicorns and counting. This is over 3 times the amount of American unicorn companies in 2020, which counted to just 83.
36. Q3 of 2022 yielded just 25 new unicorns, the lowest unicorn birth count since 2020
(CB Insights)
The rate of uber-successful startups are at a decline, and the decline of VC investments could be a contributing factor. In Q3 of 2022, the global venture capital spend on startups just suffered the largest quarterly drop in a decade of 34%. This same quarter resulted in 7,936 VC investments deals continuing a 7-quarter low.
United States startup statistics
37. Around 565,000 startups are launched each month in the U.S.
(Fundable)
Every month in the United States, over half of a million startups are launched. These startups go on to raise an average of $78,406 each, totaling about $531 billion each year.
38. The United States has almost 3x as many startups as the next 10 countries combined
(SPD Load)
Statistics showed that the United States had the highest number of startups—by almost 3 times the amount of the global leaders combined. In 2021, the U.S. was home to an approximate 63,703 startups. Second place was India with over 8,300 startups, and the United Kingdom with roughly 5,400.
39. Startups created almost 3 million jobs in the United States last year
(Statista)
Startups less than one year old generated nearly three million jobs in the United States in 2021. This is a slight decline from 2019 and 2020 where startups were responsible for creating 3.1 million jobs. The peak was in 1999 during the dot-com bubble, when startups created over 4.7 million jobs.
40. 70% of Americans would rather work for themselves than someone else
(Lending Tree)
Seven in 10 Americans would prefer to work for themselves and this figure jumps to 77% when asking millennials (aged 25 to 40). One in four Americans have considered starting a business within the past year, while a notable 37% of millennials had this dream. That makes this younger generation five times more likely to launch a startup.
General startup statistics
41. Startups only stay classified as a “startup” for about five years
(Nanoglobals)
How long does a startup stay a startup? This is a grey area since a universal definition of a “startup” is unclear, but generally, startups lose this classification after five years. This is because a startup becomes a “scaleup” after three consecutive years of 20% averaged annualized growth.
42. 5% of all global startups worldwide are in artificial intelligence
(Earthweb)
What does the future look like for startups? A solid 5 in every 100 startups classify themselves as Artifical Intelligence, or AI. Approximately 7.6% are in Fintech, 6.8% are Life Science and Healthcare, and 4.7% are in the gaming industry. About 2.1% are CleanTech and are committed to environmentally-friendly technologies.
43. Only 7% of business owners launched a startup because they could not find a job
(SBA)
Only 7.4% of business owners with employees started their company because they personally could not find a job. Over half, 56%, of these owners said that starting a business was the best way to make their own products.
44. One-third of small businesses launch with less than $5,000
(Small Biz Trends)
A recent study revealed that roughly 33% of small businesses get started with less than $5,000. However the majority, 58%, launched with less than $25,000. Money is a top concern for those considering a startup, as 65% admitted they were not fully confident they had enough money to start.
45. In a portfolio of 100 startups, a 10% success rate often pays for the 90% of startup failures
(Failory)
Startups are a risky business whether you’re launching one yourself or investing in one. But for VC’s, the juice is worth the squeeze when you can scale your investments. In a portfolio of about 100 startups, most of the fund’s returns come from one most successful startup in the bunch (hopefully a unicorn). Even if 90 of the 100 startups fail, the 10 successful companies compensate for all of the failures.
There you have it!
You just scrolled through 45 top startup failure statistics and many more facts all about this everchanging and innovative segment.
Want to learn more about how to become an entrepreneur?
Read more:
The Benefits of Online Business
Guide: Entrepreneur Mindset Strategies
The Best Online Business Courses
SOURCES:







One Response
Hi, thanks for this post. Could you share where you pulled this stat from? I’d like to read a bit about this myself – thanks! “Over 305 million startups are created every year around the globe…”